欧式聚类提取
欧式聚类提取是PCL中常用的一种分割提取方法,可以将三维点云场景按类别分割。
步骤:
首先通过pcl::VoxelGrid (filters)先对点云数据进行下采样滤波;
然后通过pcl::SACSegmentation<pcl::PointXYZ> seg; (segmentation)创建Nodelet样本细分类别;
然后通过 pcl::ExtractIndices<pcl::PointXYZ> extract;(filters)提取索引;
最后通过pcl::EuclideanClusterExtraction<pcl::PointXYZ> ec; 生成欧式聚类对象 (segmentation)。
代码实现:
#include <pcl/ModelCoefficients.h>
#include <pcl/point\_types.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd\_io.h>
#include <pcl/filters/extract\_indices.h>
#include <pcl/filters/voxel\_grid.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal\_3d.h>
#include <pcl/search/kdtree.h>
#include <pcl/sample\_consensus/method\_types.h>
#include <pcl/sample\_consensus/model\_types.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/sac\_segmentation.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/extract\_clusters.h>
int main()
{
// 读取点云数据
pcl::PCDReader reader;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>), cloud\_f(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
reader.read("data/table\_scene\_lms400.pcd", \*cloud);
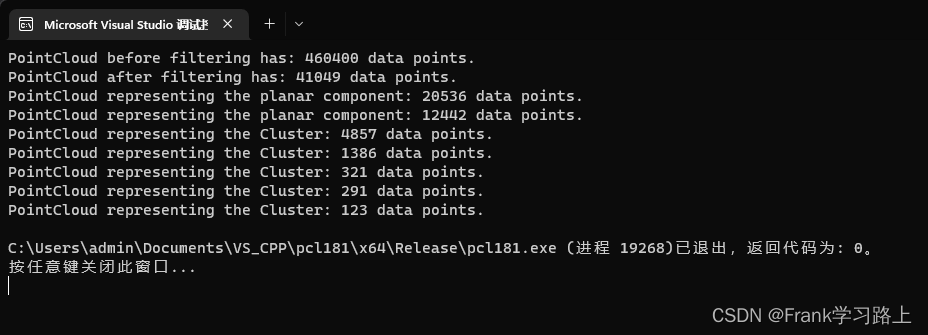
std::cout << "PointCloud before filtering has: " << cloud->size() << " data points." << std::endl;
// 创建滤波对象: 体素1cm的下采样
pcl::VoxelGrid<pcl::PointXYZ> vg;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud\_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
vg.setInputCloud(cloud);
vg.setLeafSize(0.01f, 0.01f, 0.01f);
vg.filter(\*cloud_filtered);
std::cout << "PointCloud after filtering has: " << cloud_filtered->size() << " data points." << std::endl; //\*
// 为平面模型创建分割对象,并设置所有参数
pcl::SACSegmentation<pcl::PointXYZ> seg;
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers(new pcl::PointIndices);
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients(new pcl::ModelCoefficients);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud\_plane(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>());
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true);
seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);
seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
seg.setMaxIterations(100);
seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.02);
int nr_points = (int)cloud_filtered->size();
while (cloud_filtered->size() > 0.3 \* nr_points)
{
// 从剩下的点云中分割出最大的平面成分
seg.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
seg.segment(\*inliers, \*coefficients);
if (inliers->indices.size() == 0)
{
std::cout << "Could not estimate a planar model for the given dataset." << std::endl;
break;
}
// 从输入点云中提取平面片段
pcl::ExtractIndices<pcl::PointXYZ> extract;
extract.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
extract.setIndices(inliers);
extract.setNegative(false);
// 求出与平面相关的点
extract.filter(\*cloud_plane);
std::cout << "PointCloud representing the planar component: " << cloud_plane->size() << " data points." << std::endl;
// 移除平面,提取其余部分
extract.setNegative(true);
extract.filter(\*cloud_f);
\* cloud_filtered = \*cloud_f;
}
// 为提取的搜索方法创建KdTree对象
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);
tree->setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
std::vector<pcl::PointIndices> cluster_indices;
pcl::EuclideanClusterExtraction<pcl::PointXYZ> ec;
ec.setClusterTolerance(0.02); // 2cm
ec.setMinClusterSize(100); //最小聚类尺寸
ec.setMaxClusterSize(25000); //最大聚类尺寸
ec.setSearchMethod(tree); //tree搜索方法
ec.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered); //将滤波后的点云作为输入
ec.extract(cluster_indices); //导出聚类片段数据
int j = 0;
for (const auto& cluster : cluster_indices)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud\_cluster(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
for (const auto& idx : cluster.indices) {
cloud_cluster->push\_back((\*cloud_filtered)[idx]);
} //\*
cloud_cluster->width = cloud_cluster->size();
cloud_cluster->height = 1;
cloud_cluster->is_dense = true;
std::cout << "PointCloud representing the Cluster: " << cloud_cluster->size() << " data points." << std::endl;
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "cloud\_cluster\_" << j << ".pcd";
writer.write<pcl::PointXYZ>(ss.str(), \*cloud_cluster, false); //\*
j++;
}
return 0;
}
运行结果:
在ROS中的实现,大多参照adams大佬,在这里理解一下:
项目结构如下:
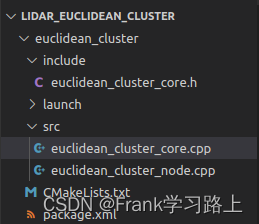
euclidean_cluster_core是算法实现,同时还定义了与ROS通信的接口,以及BoundingBox的绘制。
ROS的最小组成如下,可以参考封装其他代码:
#include "euclidean\_cluster\_core.h"
int main(int argc, char \*\*argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "euclidean\_cluster");
ros::NodeHandle nh; //nh对象
EuClusterCore core(nh); //欧式聚类处理
return 0;
}
ROS的订阅和发布如下,可根据需求更改:
EuClusterCore::EuClusterCore(ros::NodeHandle &nh)
{
seg_distance_ = {15, 30, 45, 60}; //分割距离
cluster_distance_ = {0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5}; //cluster距离
sub_point_cloud_ = nh.subscribe("/filtered\_points\_no\_ground", 5, &EuClusterCore::point_cb, this); //订阅
pub_bounding_boxs_ = nh.advertise<jsk\_recognition\_msgs::BoundingBoxArray>("/detected\_bounding\_boxs", 5); //发布
ros::spin();
}
主要的处理函数如下:
void voxel\_grid\_filer(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr in, pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr out,
double leaf_size);
void cluster\_by\_distance(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr in_pc, std::vector<Detected_Obj> &obj_list);
void cluster\_segment(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr in_pc,
double in_max_cluster_distance, std::vector<Detected_Obj> & obj_list);
void point\_cb(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr &in_cloud_ptr);
void publish\_cloud(const ros::Publisher &in_publisher,
const pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr in_cloud_to_publish_ptr,
const std_msgs::Header &in_header);
以上。