点云输入输出示例
文章目录
学习资料
最重要的参考资料是官网:https://pointclouds.org/,Docs是函数手册,Tutorials是代码示例,两者结合学习(shiyong)。
另外,有位大佬总结了PCL的相关资料,在这里,太感谢了,有学习方法和demo演示等等,跟着学就完事了。
总的来说,PCL主要是对16个模块的函数进行学习,掌握基础后,重点是要做相关项目,积累实战经验。大家都建议在Ubuntu学习,但对我而言,我却觉得在Windows下更能理解PCL相关第三方库和头文件、库目录等的配置,而且用VS调试也比较方便,因人而异吧,我是在Windows学习,然后工程化再转到Ubuntu。
点云文件格式
点云IO相关函数如下:https://pointclouds.org/documentation/group__io.html
在PCD格式出现之前,描述3D物体的格式有PLY、STL、OBJ、X3D等,但这些格式都无法满足点云在感知领域的数据处理要求,因此PCD格式诞生。
PCD文件的入口定义一般有:
VERSION
FIELDS
SIZE
TYPE
COUNT
WIDTH
HEIGHT
VIEWPOINT
POINTS
DATA
例如,对比这个例子:
# .PCD v.7 - Point Cloud Data file format
VERSION .7
FIELDS x y z rgb
SIZE 4 4 4 4
TYPE F F F F
COUNT 1 1 1 1
WIDTH 213
HEIGHT 1
VIEWPOINT 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
POINTS 213
DATA ascii
0.93773 0.33763 0 4.2108e+06
0.90805 0.35641 0 4.2108e+06
0.81915 0.32 0 4.2108e+06
0.97192 0.278 0 4.2108e+06
写入点云数据到PCD文件
创建write_pcd.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/io/pcd\_io.h> //pcd输入输出头
#include <pcl/point\_types.h> //pcd点云类型头
using namespace std;
int main()
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> cloud; //实例化模板类PointCloud,类型为PointXYZ
//写入点云数据,用随机数填充
cloud.width = 5;
cloud.height = 1;
cloud.is_dense = false; //是否是稠密型
cloud.resize(cloud.width \* cloud.height);
for (auto& point : cloud)
{
point.x = 1024 \* rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
point.y = 1024 \* rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
point.z = 1024 \* rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
}
pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII("test\_pcd.pcd", cloud);
cerr << "Saved " << cloud.size() << " data points to test\_pcd.pcd." << endl;
//cerr:输出到标准错误的ostream对象,常用于程序错误信息;
for(const auto& point: cloud)
cerr << " " << point.x << " " << point.y << " " << point.z << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果如下:

从PCD文件读取点云数据
创建pcd_read.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/io/pcd\_io.h> //pcd输入输出头
#include <pcl/point\_types.h> //pcd点云类型头
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//创建一个PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> boost共享指针并进行实例化
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
//判断点云文件是否存在
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile<pcl::PointXYZ>("test\_pcd.pcd", \*cloud) == -1)
{
PCL\_ERROR("Couldn't read file test\_pcd.pcd \n");
return (-1);
}
//转为PCD点云类型并输出
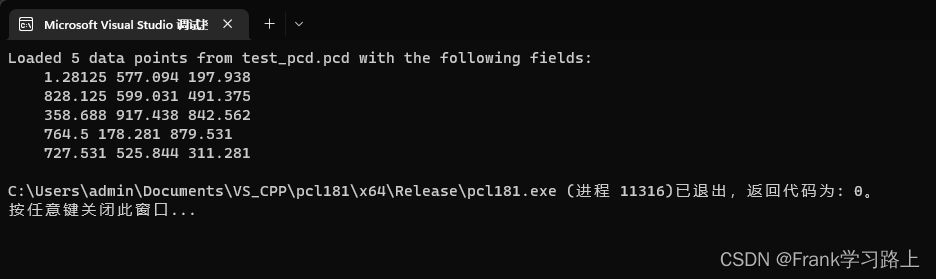
cout << "Loaded "
<< cloud->width \* cloud->height // 宽\*高
<< " data points from test\_pcd.pcd with the following fields: "
<< endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud->points.size(); ++i)
cout << " " << cloud->points[i].x
<< " " << cloud->points[i].y
<< " " << cloud->points[i].z << endl;
return (0);
}
运行结果如下:
点云拼接
点云拼接有点云连接concatenate points(纵向连接) 和字段连接concatenate fields(横向连接) 两种。
创建concatenate_clouds.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/io/pcd\_io.h> //pcd输入输出头
#include <pcl/point\_types.h> //pcd点云类型头
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char\*\* argv)
{
cout << "argc: " << argc << endl;
cout << "argv: " << argv[1] << endl;
if (argc != 2) //提示如果执行可执行文件输入两个参数 -f 或者-p
{
cerr << "please specify command line arg '-f' or '-p'" << endl;
exit(0);
}
//申明三个pcl::PointXYZ点云数据类型,分别为cloud\_a, cloud\_b, cloud\_c
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> cloud_a, cloud_b, cloud_c;
//存储进行连接时需要的Normal点云,Normal (float n\_x, float n\_y, float n\_z)
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal> n_cloud_b;
//存储连接XYZ与normal后的点云
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal> p_n_cloud_c;
// 创建点云数据
//设置cloud\_a的个数为5
cloud_a.width = 5;
cloud_a.height = cloud_b.height = n_cloud_b.height = 1; //设置都为无序点云
cloud_a.points.resize(cloud_a.width \* cloud_a.height); //总数
if (strcmp(argv[1], "-p") == 0) //判断是否为连接a+b=c(点云连接)
{
cloud_b.width = 3;
cloud_b.points.resize(cloud_b.width \* cloud_b.height);
}
else
{
n_cloud_b.width = 5; //如果是连接XYZ与normal则生成5个法线(字段间连接)
n_cloud_b.points.resize(n_cloud_b.width \* n_cloud_b.height);
}
//以下循环生成无序点云填充上面定义的两种类型的点云数据
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud_a.points.size(); ++i)
{ //cloud\_a产生三个点(每个点都有X Y Z 三个随机填充的值)
cloud_a.points[i].x = 1024 \* rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
cloud_a.points[i].y = 1024 \* rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
cloud_a.points[i].z = 1024 \* rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
}
if (strcmp(argv[1], "-p") == 0)
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud_b.points.size(); ++i)
{ //如果连接a+b=c,则cloud\_b用三个点作为xyz的数据
cloud_b.points[i].x = 1024 \* rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
cloud_b.points[i].y = 1024 \* rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
cloud_b.points[i].z = 1024 \* rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
}
else
for (size_t i = 0; i < n_cloud_b.points.size(); ++i)
{ //如果连接xyz+normal=xyznormal则n\_cloud\_b用5个点作为normal数据
n_cloud_b.points[i].normal[0] = 1024 \* rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
n_cloud_b.points[i].normal[1] = 1024 \* rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
n_cloud_b.points[i].normal[2] = 1024 \* rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
}
/\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*
定义了连接点云会用到的5个点云对象:3个输入(cloud\_a cloud\_b 和n\_cloud\_b)
两个输出(cloud\_c n\_cloud\_c)然后为两个输入点云cloud\_a和 cloud\_b或者cloud\_a 和n\_cloud\_b填充数据
\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*\*/
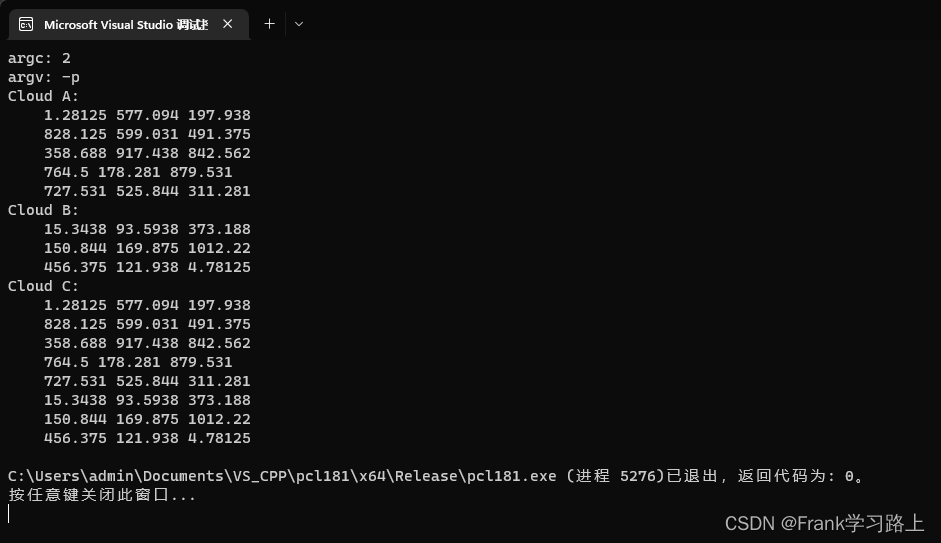
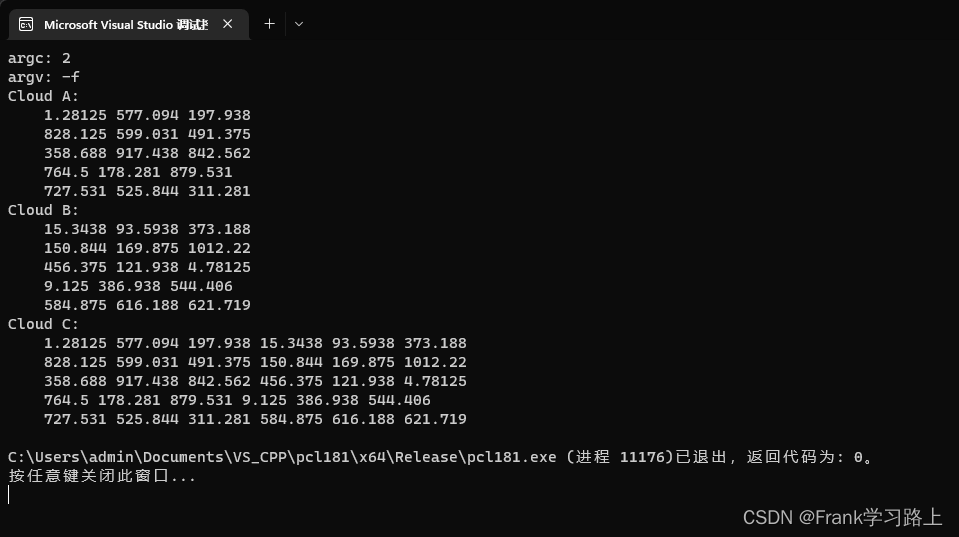
//输出Cloud A
cerr << "Cloud A: " << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud_a.points.size(); ++i)
cerr << " " << cloud_a.points[i].x << " " << cloud_a.points[i].y << " " << cloud_a.points[i].z << endl;
//输出Cloud B
cerr << "Cloud B: " << endl;
if (strcmp(argv[1], "-p") == 0)
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud_b.points.size(); ++i)
cerr << " " << cloud_b.points[i].x << " " << cloud_b.points[i].y << " " << cloud_b.points[i].z << endl;
else //输出n\_Cloud\_b
for (size_t i = 0; i < n_cloud_b.points.size(); ++i)
cerr << " " << n_cloud_b.points[i].normal[0] << " " << n_cloud_b.points[i].normal[1] << " " << n_cloud_b.points[i].normal[2] << endl;
// 两种方式
if (strcmp(argv[1], "-p") == 0)
{
cloud_c = cloud_a;
cloud_c += cloud_b; //连接点云 (把cloud\_a和cloud\_b连接一起创建cloud\_c后输出)
cerr << "Cloud C: " << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud_c.points.size(); ++i)
cerr << " " << cloud_c.points[i].x << " " << cloud_c.points[i].y << " " << cloud_c.points[i].z << " " << endl;
}
else
{ //连接字段 (把cloud\_a和 n\_cloud\_b字段连接 一起创建 p\_n\_cloud\_c)
pcl::concatenateFields(cloud_a, n_cloud_b, p_n_cloud_c);
cerr << "Cloud C: " << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < p_n_cloud_c.points.size(); ++i)
cerr << " " << p_n_cloud_c.points[i].x << " " << p_n_cloud_c.points[i].y << " " << p_n_cloud_c.points[i].z << " " << p_n_cloud_c.points[i].normal[0] << " " << p_n_cloud_c.points[i].normal[1] << " " << p_n_cloud_c.points[i].normal[2] << endl;
}
return (0);
}
运行点云连接-p:
运行字段连接-f:
以上。