Poco可移植组件库配置与使用
😏★,°:.☆( ̄▽ ̄)/$:.°★ 😏
这篇文章主要介绍Poco可移植组件库配置与使用。
无专精则不能成,无涉猎则不能通。——梁启超
欢迎来到我的博客,一起学习,共同进步。
喜欢的朋友可以关注一下,下次更新不迷路🥞
文章目录
😏1. 项目介绍
项目Github地址:https://github.com/pocoproject/poco
官网:https://pocoproject.org/
Poco是一个功能丰富、易于使用的跨平台C++开发框架,全称为”POrtable COmponents“,它提供了一系列的类库和工具,用于开发跨平台、高性能、可扩展的应用程序。
以下是Poco库的一些主要特点和功能:
1.跨平台支持:Poco库支持多个操作系统,包括Windows、Linux、macOS等,使得开发者可以编写可移植的代码。它提供了对操作系统API的抽象和封装,简化了跨平台开发过程。
2.组件化设计:Poco库的设计基于组件化思想,将常用的功能封装成独立的可重用组件。每个组件都提供了清晰而一致的接口,开发者可以根据需要选择并使用适当的组件。
3.网络和通信:Poco库提供了强大而易用的网络和通信功能,包括HTTP、SMTP、POP3、FTP、WebSocket、TCP/UDP等协议的支持,以及HTTP服务器和客户端的实现。
4.数据库访问:Poco库具有对多种数据库的支持,包括MySQL、SQLite、PostgreSQL、Oracle等。它提供了简单而灵活的接口,方便进行数据库连接、查询和事务处理。
5.加密和安全:Poco库提供了包括AES、RSA、HMAC、SSL等在内的各种加密算法的支持,以及摘要、签名、证书管理等安全功能。
6.多线程和并发:Poco库提供了多线程和并发编程的支持,包括线程、互斥锁、条件变量、线程池等工具,方便编写高效的并发代码。
7.XML和JSON处理:Poco库提供了对XML和JSON格式的解析、生成和处理的支持,方便开发者进行配置文件解析、数据交换等操作。
8.文件系统和IO操作:Poco库提供了强大的文件系统和IO操作功能,包括文件读写、目录遍历、文件监控等,简化了文件和目录处理的过程。
9.单元测试和文档生成:Poco库内置了用于单元测试和文档生成的工具集,方便开发者进行代码测试、文档编写和生成。
😊2. 环境配置
下面进行环境配置:
Windows
cd poco
mkdir cmake-build
# 进入build并编译
cd cmake-build
cmake ..
# 管理员身份运行
# 生成lib
cmake --build . --config Release
# 安装
cmake --build . --target install
Ubuntu
# apt安装
sudo apt install libpoco-dev
# 源码安装
# 安装依赖
sudo apt-get install -y g++ make openssl libssl-dev
# 下载解压
wget https://pocoproject.org/releases/poco-1.11.0/poco-1.11.0-all.tar.gz
tar -xvf poco-1.11.0-all.tar.gz
# 编译
cd poco-1.11.0-all
./configure --no-tests --no-samples
cd build
cmake .. && make
sudo make install
程序编译与运行:
# 链接需要用到的组件,-lPocoFoundation -lPocoUtil -lPocoNet -lPocoXML是4个基本组件
g++ -o main main.cpp -lPocoFoundation -lPocoUtil -lPocoNet -lPocoJSON && ./main
😆3. 使用说明
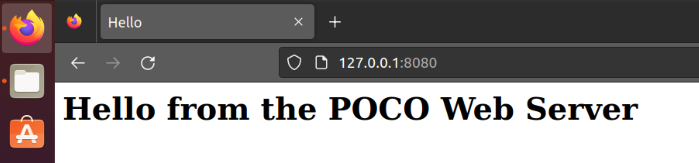
web服务示例
官方示例,实现了一个简单的多线程web服务器,为单个HTML页面提供服务,使用Foundation, Net和Util库,生成的网页在8080端口:
#include "Poco/Net/HTTPServer.h"
#include "Poco/Net/HTTPRequestHandler.h"
#include "Poco/Net/HTTPRequestHandlerFactory.h"
#include "Poco/Net/HTTPServerRequest.h"
#include "Poco/Net/HTTPServerResponse.h"
#include "Poco/Net/ServerSocket.h"
#include "Poco/Util/ServerApplication.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace Poco;
using namespace Poco::Net;
using namespace Poco::Util;
class HelloRequestHandler: public HTTPRequestHandler
{
void handleRequest(HTTPServerRequest& request, HTTPServerResponse& response)
{
Application& app = Application::instance();
app.logger().information("Request from %s", request.clientAddress().toString());
response.setChunkedTransferEncoding(true);
response.setContentType("text/html");
response.send()
<< "<html>"
<< "<head><title>Hello</title></head>"
<< "<body><h1>Hello from the POCO Web Server</h1></body>"
<< "</html>";
}
};
class HelloRequestHandlerFactory: public HTTPRequestHandlerFactory
{
HTTPRequestHandler\* createRequestHandler(const HTTPServerRequest&)
{
return new HelloRequestHandler;
}
};
class WebServerApp: public ServerApplication
{
void initialize(Application& self)
{
loadConfiguration();
ServerApplication::initialize(self);
}
int main(const std::vector<std::string>&)
{
UInt16 port = static\_cast<UInt16>(config().getUInt("port", 8080));
HTTPServer srv(new HelloRequestHandlerFactory, port);
srv.start();
logger().information("HTTP Server started on port %hu.", port);
waitForTerminationRequest();
logger().information("Stopping HTTP Server...");
srv.stop();
return Application::EXIT_OK;
}
};
POCO\_SERVER\_MAIN(WebServerApp)
编译运行:
g++ -o main main.cpp -lPocoFoundation -lPocoNet -lPocoUtil && ./main
Json解析示例
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "Poco/JSON/Object.h"
#include "Poco/JSON/Parser.h"
#include "Poco/Dynamic/Var.h"
#include "Poco/JSON/Stringifier.h"
int main()
{
/\* 解析json & 从文件中解析json \*/
std::string jsonString = R"({"name": "John", "age": 30, "city": "New York"})";
// std::ifstream file("data.json");
// if (!file.is\_open()) {
// std::cerr << "Failed to open file." << std::endl;
// return 1;
// }
// std::string jsonString((std::istreambuf\_iterator<char>(file)), std::istreambuf\_iterator<char>());
// 创建 JSON 解析器
Poco::JSON::Parser parser;
Poco::Dynamic::Var result;
try {
// 解析 JSON 字符串
result = parser.parse(jsonString);
} catch (const Poco::Exception& ex) {
std::cerr << "JSON parsing error: " << ex.displayText() << std::endl;
return 1;
}
// 将解析结果转换为 Poco::JSON::Object 类型
Poco::JSON::Object::Ptr object = result.extract<Poco::JSON::Object::Ptr>();
// 获取和操作 JSON 对象中的值
std::string name = object->getValue<std::string>("name");
int age = object->getValue<int>("age");
std::string city = object->getValue<std::string>("city");
// 打印结果
std::cout << "Name: " << name << std::endl;
std::cout << "Age: " << age << std::endl;
std::cout << "City: " << city << std::endl;
/\* 生成json & 写入到json文件 \*/
// 创建 JSON 对象
Poco::JSON::Object jsonObject;
// 添加键值对
jsonObject.set("name", "John");
jsonObject.set("age", 30);
jsonObject.set("city", "New York");
// 将 JSON 对象转换为字符串
std::ostringstream oss;
Poco::JSON::Stringifier::stringify(jsonObject, oss);
std::string jsonString2 = oss.str();
// 打印生成的 JSON 字符串
std::cout << jsonString2 << std::endl;
// // 写入 JSON 字符串到文件
// std::ofstream file("data.json");
// if (file.is\_open()) {
// file << jsonString2;
// file.close();
// std::cout << "JSON data has been written to file." << std::endl;
// } else {
// std::cerr << "Failed to open file." << std::endl;
// return 1;
// }
return 0;
}
多线程示例:
#include <iostream>
#include "Poco/Thread.h"
#include "Poco/Runnable.h"
class MyTask : public Poco::Runnable
{
public:
void run() override
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
std::cout << "Thread ID: " << Poco::Thread::currentTid()
<< " Task ID: " << i << std::endl;
Poco::Thread::sleep(1000);
}
}
};
int main()
{
// 创建线程任务对象
MyTask task;
// 创建线程对象并启动
Poco::Thread thread;
thread.start(task);
// 主线程继续执行其他任务
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
std::cout << "Main Thread ID: " << Poco::Thread::currentTid()
<< " Main Task ID: " << i << std::endl;
Poco::Thread::sleep(500);
}
// 等待子线程结束
thread.join();
return 0;
}
日期时间示例
#include <iostream>
#include "Poco/DateTime.h"
#include "Poco/DateTimeFormatter.h"
int main()
{
// 获取当前日期和时间
Poco::DateTime now;
// 格式化日期和时间为字符串
std::string formattedDateTime = Poco::DateTimeFormatter::format(now, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S");
// 输出格式化后的日期和时间
std::cout << "Formatted Date and Time: " << formattedDateTime << std::endl;
// 获取日期部分
Poco::DateTime date(now.year(), now.month(), now.day());
// 格式化日期为字符串
std::string formattedDate = Poco::DateTimeFormatter::format(date, "%Y-%m-%d");
// 输出格式化后的日期
std::cout << "Formatted Date: " << formattedDate << std::endl;
return 0;
}
生成uuid示例
#include <iostream>
#include "Poco/UUIDGenerator.h"
#include "Poco/UUID.h"
int main()
{
// 使用默认的UUID生成器
Poco::UUIDGenerator generator;
// 生成一个随机UUID
Poco::UUID uuid1 = generator.createRandom();
// 生成一个基于时间的UUID
Poco::UUID uuid2 = generator.createOne();
// 输出UUID
std::cout << "Random UUID: " << uuid1.toString() << std::endl;
std::cout << "Time-based UUID: " << uuid2.toString() << std::endl;
return 0;
}

以上。