AStar规划算法原理与实现
😏★,°:.☆( ̄▽ ̄)/$:.°★ 😏
这篇文章主要介绍AStar规划算法原理与实现。
学其所用,用其所学。——梁启超
欢迎来到我的博客,一起学习,共同进步。
喜欢的朋友可以关注一下,下次更新不迷路🥞
文章目录
😏1. AStar算法介绍
A* 算法(A-Star Algorithm)是一种用于图形路径搜索和图形遍历的启发式搜索算法。它结合了Dijkstra算法的广度优先搜索和启发式函数(即估计函数),以找到从起点到目标点的最优路径。A* 算法在计算机科学和人工智能领域广泛应用,特别是在路径规划、游戏开发、机器人控制等领域。
A* 算法的基本思想是在搜索过程中维护两个值:g(n) 和 h(n)。其中,g(n) 表示从起点到当前节点 n 的实际代价,h(n) 表示从当前节点 n 到目标节点的估计代价。A* 算法的目标是找到一条路径,使得 f(n) = g(n) + h(n) 最小,其中 n 表示路径上的节点。
A* 算法的工作过程如下:
1.初始化起点和终点。
2.将起点加入开放列表(Open List)。
3.重复以下步骤,直到达到终点或开放列表为空:
- 从开放列表中选择一个节点 n,该节点具有最小的 f(n) 值。
- 如果节点 n 是终点,则路径已找到,跳转到步骤 6。
- 将节点 n 从开放列表中移除,并加入关闭列表(Closed List)。
- 对节点 n 的所有相邻节点进行以下操作:
- 如果相邻节点不可通过或已在关闭列表中,则忽略它。
- 如果相邻节点不在开放列表中,则将其加入开放列表,并计算它的代价值 g(n) 和启发式值 h(n)。
- 如果相邻节点已经在开放列表中,检查从当前节点 n 到该相邻节点的路径是否更优(即 g(n) 值更小)。如果是,则更新相邻节点的父节点为当前节点 n,并重新计算 g(n) 值。
4. 如果开放列表为空,表示无法找到路径,搜索失败。
5. 重构路径:从终点开始,沿着每个节点的父节点回溯,直到回溯到起点,形成最优路径。
6. 返回最优路径。
A* 算法的关键在于启发式函数 h(n),它用于估计从当前节点 n 到目标节点的代价。启发式函数需要满足两个条件:首先,它必须能够估计出当前节点 n 到目标节点的实际代价的下界(即不会高估代价);其次,它应该是快速计算的,以便在搜索过程中进行实时更新。
常用的启发式函数包括曼哈顿距离(Manhattan Distance)、欧几里得距离(Euclidean Distance)和对角线距离(Diagonal Distance)等。
A* 算法的优点在于它能够在保证找到最优路径的前提下,避免对整个搜索空间进行完全遍历,从而提高了搜索效率。然而,A* 算法的性能也受到启发式函数的选择和问题的特性影响,不同的启发式函数可能会导致不同的搜索结果。
😆2. C++实现示例
Github项目地址(仅学习用):https://github.com/JokerEyeAdas/AStarShellMapSearch
编译运行:g++ CAstar.cpp AStarTest.cpp -o AstarShellMapTest

该案例实现了在shell终端中显示10*10的地图,设置起点和终点,用寻路函数执行,若能找到全局路径,则用绿色的块表示路径,否则不显示并提示有障碍物。
由这个文件组成:ShellMap.hpp、CAstar.h、CAstar.cpp和AStarTest.cpp组成。
CAstar.h定义了障碍类型和openlist&closelist,以及f=g+h评价函数:
#ifndef __Astar__CAstar__
#define __Astar__CAstar__
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include "ShellMap.hpp"
using namespace std;
//地图最大值
#define MAX_X 10
#define MAX_Y 10
enum class AType
{
ATYPE_UNKNOWN,
ATYPE_CLOSED,
ATYPE_OPENED,
ATYPE_BARRIER //障碍
};
class APoint
{
public:
APoint();
~APoint();
int x;
int y;
AType type; //类型:障碍、开放列表、关闭列表
int f; //f = g+h
int g;
int h;
APoint *parent;
bool operator == (const APoint& po)
{
if (x == po.x && y == po.y)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
class CAstar
{
vector<APoint*> _openList; //开放列表
vector<APoint*> _closeList; //关闭列表
vector<APoint*> _neighbourList; //周边节点
APoint* _endPoint;
APoint* _curPoint;
vector< vector<APoint*> > _allPoints;
ShellMap shellMap_;
public:
CAstar();
~CAstar();
APoint* findWay(APoint* beginPoint,APoint* endPoint,vector< vector<APoint*> >& allPoints);
ShellMap& GetMap() {return shellMap_;};
// APoint* findWay(int beginX,int beginY,int endX,int endY);
private:
int getF(APoint *point);
int getH(APoint *point);
vector<APoint*> getNeighboringPoint(APoint* point);
};
#endif
CAstar.cpp主要是启发函数的实现:
#include "CAstar.h"
bool mySort(const APoint* p1,const APoint* p2)
{
return p1->f < p2->f;
}
APoint::APoint():x(0)
,y(0)
,h(0)
,f(0)
,g(0)
,parent(nullptr)
,type(AType::ATYPE_UNKNOWN)
{
}
APoint::~APoint()
{
}
#pragma mark------CAstar-------
CAstar::CAstar():_endPoint(nullptr)
,_curPoint(nullptr)
{
shellMap_.GenMap(MAX_X, MAX_Y);
//shellMap_.SetStartEndPoint(Point(1, 1), Point(6, 6));
}
CAstar::~CAstar()
{
_openList.clear();
_closeList.clear();
_neighbourList.clear();
_allPoints.clear();
}
APoint* CAstar::findWay(APoint *beginPoint, APoint *endPoint,vector< vector<APoint*> >& allPoints)
{
shellMap_.SetStartEndPoint(Point(beginPoint->x, beginPoint->y), Point(endPoint->x, endPoint->y));
shellMap_.ShowMap();
//传递地图
_allPoints = allPoints;
_endPoint = endPoint;
if (_endPoint->type == AType::ATYPE_BARRIER)
{
cout<<"ERR the final point is barrier!!"<<endl;
return nullptr;
}
if (*_endPoint == *beginPoint)
{
cout<<"起始点相同"<<endl;
return nullptr;
}
_openList.push_back(beginPoint);
beginPoint->type = AType::ATYPE_OPENED;
beginPoint->f = getF(beginPoint);
do
{
//获取最小值的节点
_curPoint = _openList[0];
_openList.erase(_openList.begin());
_curPoint->type = AType::ATYPE_CLOSED;
_closeList.push_back(_curPoint);
//GetMap().GetMapPtr()[_curPoint->y * MAX_X + _curPoint->x] = CUR;
if (*_curPoint == *_endPoint)
{
cout<<"have find way"<<endl;
return _curPoint;
}
//获取相邻的节点
vector<APoint*> neVec = getNeighboringPoint(_curPoint);
for (int i = 0; i<neVec.size(); i++)
{
auto tmpoint = neVec[i];
if (tmpoint->type == AType::ATYPE_CLOSED)
{
//GetMap().GetMapPtr()[tmpoint->y * MAX_X + tmpoint->x] = CLOSE;
continue;
}
//是否在开放列表里
if (tmpoint->type != AType::ATYPE_OPENED)
{
tmpoint->parent = _curPoint;
tmpoint->g = _curPoint->g + 10;
//计算H值
tmpoint->h = getH(tmpoint);
//添加到开放列表里
_openList.push_back(tmpoint);
tmpoint->type = AType::ATYPE_OPENED;
//GetMap().GetMapPtr()[tmpoint->y * MAX_X + tmpoint->x] = OPEN;
}
else
{
//已经在开放列表里
if (tmpoint->h < _curPoint->h)
{
tmpoint->parent = _curPoint;
tmpoint->g = _curPoint->g + 10;
//GetMap().GetMapPtr()[tmpoint->y * MAX_X + tmpoint->x] = OPEN;
}
}
}
//排序 F值最小的排在前面
sort(_openList.begin(), _openList.end(), mySort);
//GetMap().ShowMap();
//sleep(500);
} while (_openList.size()>0);
cout<<"---can not find way---"<<endl;
return nullptr;
}
int CAstar::getF(APoint *point)
{
return (point->g + getH(point));
}
int CAstar::getH(APoint *point)
{
//曼哈顿城市街区估算法
return (abs(_endPoint->y - point->y) + abs(_endPoint->x - point->x))*10;
}
vector<APoint*> CAstar::getNeighboringPoint(APoint *point)
{
_neighbourList.clear();
// cout<<"nei size:"<<_neighbourList.size()<<endl;
if (point->x < MAX_X-1)
{
if (_allPoints[point->x+1][point->y]->type != AType::ATYPE_BARRIER)
{
_neighbourList.push_back(_allPoints[point->x+1][point->y]);
}
}
if (point->x >0)
{
if (_allPoints[point->x-1][point->y]->type != AType::ATYPE_BARRIER)
{
_neighbourList.push_back(_allPoints[point->x-1][point->y]);
}
}
if (point->y < MAX_Y-1)
{
if (_allPoints[point->x][point->y+1]->type != AType::ATYPE_BARRIER)
{
_neighbourList.push_back(_allPoints[point->x][point->y+1]);
}
}
if (point->y >0)
{
if (_allPoints[point->x][point->y-1]->type != AType::ATYPE_BARRIER)
{
_neighbourList.push_back(_allPoints[point->x][point->y-1]);
}
}
return _neighbourList;
}
AStarTest.cpp是测试示例:
#include "CAstar.h"
int main()
{
/*ShellMap map(10, 10);
map.SetStartEndPoint(Point(1, 1), Point(8, 8));
map.ShowMap();
*/
auto star = new CAstar();
vector< vector<APoint*> > map;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_X; i++)
{
vector<APoint*> tmp;
for (int j = 0; j < MAX_Y; j++)
{
APoint *point = new APoint();
point->x = i;
point->y = j;
if (star->GetMap().GetMapPtr()[j * MAX_X + i] == BLOCK)
{
point->type = AType::ATYPE_BARRIER;
}
tmp.push_back(point);
}
map.push_back(tmp);
}
//开始寻路
auto point = star->findWay(map[0][0], map[9][9], map);
if (!point)
{
return 0;
}
while (point)
{
if (star->GetMap().GetMapPtr()[point->y * MAX_X + point->x] == START || star->GetMap().GetMapPtr()[point->y * MAX_X + point->x] == END) {
;
} else {
star->GetMap().GetMapPtr()[point->y * MAX_X + point->x] = PATH;
}
point = point->parent;
}
star->GetMap().ShowMap();
//-------------释放内存----------
delete star;
for (int i = 0; i<MAX_X; i++)
{
for (int j = 10; j<MAX_Y; j++)
{
delete map[i][j];
map[i][j] = nullptr;
}
}
return 0;
}
另一个示例是编译成so库的,对pgm图进行路径搜索:https://github.com/Eurecat/astar-gridmap-2d
😆3. ROS实现示例
混合A*算法ROS实现示例-Github地址:https://github.com/zm0612/Hybrid_A_Star
可在Rviz中进行仿真,通过设置起点和终点,算法将进行规划并生成路径,适合算法学习。
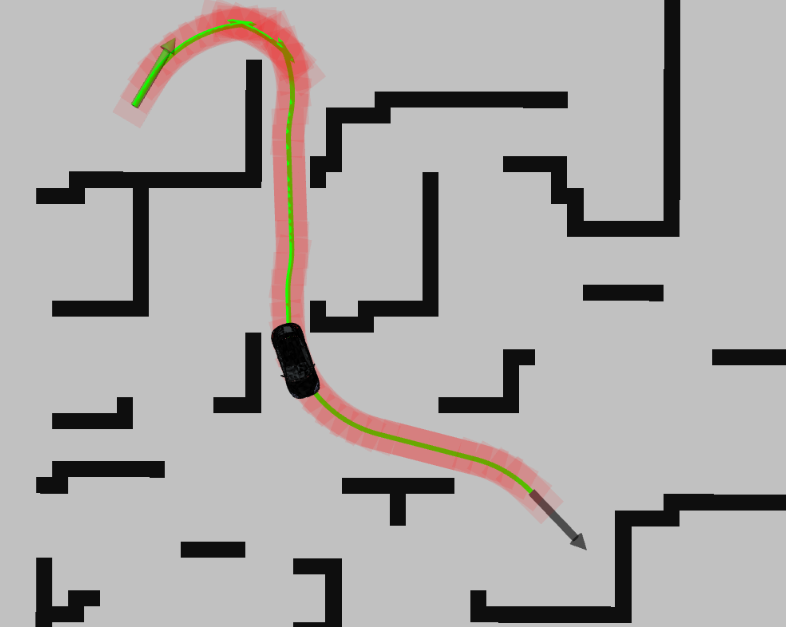
😆4. 其他参考
规划与曲线生成项目Github地址:https://github.com/czjaixuexi/path_planning
该项目实现了astar、dijkstra、rrt规划算法和bezier、b-spline曲线生成,并用matplotlibcpp.h调用python的matplot库实现了图形化显示,清楚地展示了规划算法和曲线的生成过程,可以学习。
规控算法项目Github地址:https://github.com/onlytailei/CppRobotics
EMPlanner项目Github地址:https://github.com/reflector-li/EMplanner
EM planner是百度Apollo自动驾驶系统的路径规划算法。通过将非凸轨迹规划问题分解为路径规划和速度规划两个子问题,并基于matplotlibcpp.h实现可视化显示规划器的基本功能。

以上。
A*算法主要由两个部分组成:全局路径规划和局部路径规划。
文章目录
1. A*全局
全局路径规划的主要目标是在地图中找到从起点到目标点的最短路径。Autoware全局路径规划主要由以下两个部分组成:
- 车辆当前位置和目标位置的获取:通过 ROS 中的 tf 库获取车辆当前的位置和目标位置的坐标。
- A*算法的实现:主要需要完成以下几个步骤:
- 定义节点:在 A* 算法中,节点包含了当前位置、到达当前位置的代价、到达当前位置的上一个节点等信息。
- 初始化起点:将起点设置为起始节点,并将其加入到开启列表中。
- 搜索路径:在开启列表中,选择 f 值最小的节点作为当前节点。然后,将当前节点从开启列表中移除,并将其加入到关闭列表中。接着,检查当前节点是否为目标节点,如果是,则搜索完成,否则,将当前节点周围的节点加入到开启列表中,并计算它们的 f 值。最后,将当前节点设置为上一个节点,重新选择 f 值最小的节点进行搜索。
- 生成路径:在搜索完成后,可以通过从目标节点向上查找每个节点的上一个节点,从而生成一条最短路径。
2. A*局部
局部路径规划的主要目标是在当前位置和目标位置之间找到一条可行的、避开障碍物的路径。Autoware 中的局部路径规划主要由以下两个部分组成:
- 障碍物检测:使用激光雷达或摄像头等传感器检测当前车辆周围障碍物。
- A* 算法的实现:主要需要完成以下几个步骤:
- 定义节点:在 A* 算法中,节点包含了当前位置、到达当前位置的代价、到达当前位置的上一个节点等信息。
- 初始化起点:将当前位置设置为起始节点,并将其加入到开启列表中。
- 搜索路径:在开启列表中,选择 f 值最小的节点作为当前节点。然后,将当前节点从开启列表中移除,并将其加入到关闭列表中。接着,检查当前节点是否为目标节点,如果是,则搜索完成,否则,将当前节点周围的节点
3. 相关代码
setStartNode()设置起始节点并将其加入到openlist:
bool AstarSearch::setStartNode(const geometry_msgs::Pose& start_pose)
{
// Get index of start pose
int index_x, index_y, index_theta;
start_pose_local_.pose = start_pose;
poseToIndex(start_pose_local_.pose, &index_x, &index_y, &index_theta);
SimpleNode start_sn(index_x, index_y, index_theta, 0, 0);
// Check if start is valid
if (isOutOfRange(index_x, index_y) || detectCollision(start_sn))
{
return false;
}
// Set start node
AstarNode& start_node = nodes_[index_y][index_x][index_theta];
start_node.x = start_pose_local_.pose.position.x;
start_node.y = start_pose_local_.pose.position.y;
start_node.theta = 2.0 * M_PI / theta_size_ * index_theta;
start_node.gc = 0;
start_node.move_distance = 0;
start_node.back = false;
start_node.status = STATUS::OPEN;
start_node.parent = NULL;
// set euclidean distance heuristic cost
if (!use_wavefront_heuristic_ && !use_potential_heuristic_)
{
start_node.hc = calcDistance(start_pose_local_.pose.position.x, start_pose_local_.pose.position.y,
goal_pose_local_.pose.position.x, goal_pose_local_.pose.position.y) *
distance_heuristic_weight_;
}
else if (use_potential_heuristic_)
{
start_node.gc += start_node.hc;
start_node.hc += calcDistance(start_pose_local_.pose.position.x, start_pose_local_.pose.position.y,
goal_pose_local_.pose.position.x, goal_pose_local_.pose.position.y) +
distance_heuristic_weight_;
}
// Push start node to openlist
start_sn.cost = start_node.gc + start_node.hc;
openlist_.push(start_sn);
return true;
}
search()搜索路径:
bool AstarSearch::search()
{
ros::WallTime begin = ros::WallTime::now();
// Start A* search
// If the openlist is empty, search failed
while (!openlist_.empty())
{
// Check time and terminate if the search reaches the time limit
ros::WallTime now = ros::WallTime::now();
double msec = (now - begin).toSec() * 1000.0;
if (msec > time_limit_)
{
// ROS_WARN("Exceed time limit of %lf [ms]", time_limit_);
return false;
}
// Pop minimum cost node from openlist
SimpleNode top_sn = openlist_.top();
openlist_.pop();
// Expand nodes from this node
AstarNode* current_an = &nodes_[top_sn.index_y][top_sn.index_x][top_sn.index_theta];
current_an->status = STATUS::CLOSED;
// Goal check
if (isGoal(current_an->x, current_an->y, current_an->theta))
{
// ROS_INFO("Search time: %lf [msec]", (now - begin).toSec() * 1000.0);
setPath(top_sn);
return true;
}
// Expand nodes
for (const auto& state : state_update_table_[top_sn.index_theta])
{
// Next state
double next_x = current_an->x + state.shift_x;
double next_y = current_an->y + state.shift_y;
double next_theta = modifyTheta(current_an->theta + state.rotation);
double move_cost = state.step;
double move_distance = current_an->move_distance + state.step;
// Increase reverse cost
if (state.back != current_an->back)
move_cost *= reverse_weight_;
// Calculate index of the next state
SimpleNode next_sn;
geometry_msgs::Point next_pos;
next_pos.x = next_x;
next_pos.y = next_y;
pointToIndex(next_pos, &next_sn.index_x, &next_sn.index_y);
next_sn.index_theta = top_sn.index_theta + state.index_theta;
// Avoid invalid index
next_sn.index_theta = (next_sn.index_theta + theta_size_) % theta_size_;
// Check if the index is valid
if (isOutOfRange(next_sn.index_x, next_sn.index_y) || detectCollision(next_sn))
{
continue;
}
AstarNode* next_an = &nodes_[next_sn.index_y][next_sn.index_x][next_sn.index_theta];
double next_gc = current_an->gc + move_cost;
double next_hc = nodes_[next_sn.index_y][next_sn.index_x][0].hc; // wavefront or distance transform heuristic
// increase the cost with euclidean distance
if (use_potential_heuristic_)
{
next_gc += nodes_[next_sn.index_y][next_sn.index_x][0].hc;
next_hc += calcDistance(next_x, next_y, goal_pose_local_.pose.position.x, goal_pose_local_.pose.position.y) *
distance_heuristic_weight_;
}
// increase the cost with euclidean distance
if (!use_wavefront_heuristic_ && !use_potential_heuristic_)
{
next_hc = calcDistance(next_x, next_y, goal_pose_local_.pose.position.x, goal_pose_local_.pose.position.y) *
distance_heuristic_weight_;
}
// NONE
if (next_an->status == STATUS::NONE)
{
next_an->status = STATUS::OPEN;
next_an->x = next_x;
next_an->y = next_y;
next_an->theta = next_theta;
next_an->gc = next_gc;
next_an->hc = next_hc;
next_an->move_distance = move_distance;
next_an->back = state.back;
next_an->parent = current_an;
next_sn.cost = next_an->gc + next_an->hc;
openlist_.push(next_sn);
continue;
}
// OPEN or CLOSED
if (next_an->status == STATUS::OPEN || next_an->status == STATUS::CLOSED)
{
if (next_gc < next_an->gc)
{
next_an->status = STATUS::OPEN;
next_an->x = next_x;
next_an->y = next_y;
next_an->theta = next_theta;
next_an->gc = next_gc;
next_an->hc = next_hc; // already calculated ?
next_an->move_distance = move_distance;
next_an->back = state.back;
next_an->parent = current_an;
next_sn.cost = next_an->gc + next_an->hc;
openlist_.push(next_sn);
continue;
}
}
} // state update
}
// Failed to find path
// ROS_INFO("Open list is empty...");
return false;
}
isGoal()判断是否是目标节点:
bool AstarSearch::isGoal(double x, double y, double theta)
{
// To reduce computation time, we use square value for distance
static const double lateral_goal_range =
lateral_goal_range_ / 2.0; // [meter], divide by 2 means we check left and right
static const double longitudinal_goal_range =
longitudinal_goal_range_ / 2.0; // [meter], check only behind of the goal
static const double goal_angle = M_PI * (angle_goal_range_ / 2.0) / 180.0; // degrees -> radian
// Calculate the node coordinate seen from the goal point
tf::Point p(x, y, 0);
geometry_msgs::Point relative_node_point = calcRelativeCoordinate(goal_pose_local_.pose, p);
// Check Pose of goal
if (relative_node_point.x < 0 && // shoud be behind of goal
std::fabs(relative_node_point.x) < longitudinal_goal_range &&
std::fabs(relative_node_point.y) < lateral_goal_range)
{
// Check the orientation of goal
if (calcDiffOfRadian(goal_yaw_, theta) < goal_angle)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
以上。