OpenPlanner规划节点
😏1. 决策规划模块介绍
决策规划模块是自动驾驶系统的关键部分,负责根据感知和定位信息规划出车辆的行驶轨迹并在行驶中进行运动规划和决策。
Autoware的决策规划模块主要包括以下几个重要组件:
waypoint_maker:即路点生成模块,包含waypoint_saver、waypoint_loader和waypoint_marker_publisher等节点,用于路径点的保存、加载和发布等功能。
waypoint_planner:即路点规划模块,包含astar_avoid、velocity_set节点,用于局部路径规划和速度设置等功能。
lattice_planner:lattice规划模块,包含lattice_trajectory_gen、lattice_twist_convert、path_select和lattice_velocity_set节点,用于局部轨迹生成,速度设置,指令转换等功能。
😊2. lattice_planner模块
Lattice Planner 是一种基于栅格地图的规划算法,通过搜索和优化实现路径规划的目的。Lattice Planner 的核心思想是将路径规划问题转化为一系列离散化的决策问题,通过搜索和优化得到最优路径(多条路径撒点)。
与传统的A*算法不同,Lattice Planner 能够考虑车辆的动力学约束、道路限制和障碍物等因素,生成更加平滑且安全的路径。实际应用中,Lattice主要用于自主停车、避障等功能。算法示意图如下:
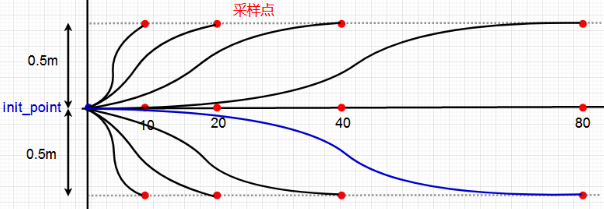
waypointTrajectory根据当前位姿、速度、路径点等信息生成预测轨迹:
static union Spline waypointTrajectory(union State veh, union State goal, union Spline curvature, int next_waypoint)
{
curvature.success=TRUE;
bool convergence=FALSE;
int iteration = 0;
union State veh_next;
double dt = step_size;
veh.v=goal.v;
// While loop for computing trajectory parameters
while(convergence == FALSE && iteration<4)
{
// Set time horizon
double horizon = curvature.s/veh.vdes;
ROS_INFO_STREAM("vdes: " << veh.vdes);
ROS_INFO_STREAM("horizon: " << horizon);
// Run motion model
veh_next = motionModel(veh, goal, curvature, dt, horizon, 0);
// Determine convergence criteria
convergence = checkConvergence(veh_next, goal);
// If the motion model doesn't get us to the goal compute new parameters
if(convergence==FALSE)
{
// Update parameters
curvature = generateCorrection(veh, veh_next, goal, curvature, dt, horizon);
iteration++;
// Escape route for poorly conditioned Jacobian
if(curvature.success==FALSE)
{
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Init State: sx "<<veh.sx<<" sy " <<veh.sy<<" theta "<<veh.theta<<" kappa "<<veh.kappa<<" v "<<veh.v);
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Goal State: sx "<<goal.sx<<" sy " <<goal.sy<<" theta "<<goal.theta<<" kappa "<<goal.kappa<<" v"<<goal.v);
break;
}
}
}
if(convergence==FALSE)
{
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Next State: sx "<<veh_next.sx<<" sy " <<veh_next.sy<<" theta "<<veh_next.theta<<" kappa "<<veh_next.kappa<<" v "<<veh_next.v);
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Init State: sx "<<veh.sx<<" sy " <<veh.sy<<" theta "<<veh.theta<<" kappa "<<veh.kappa);
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Goal State: sx "<<goal.sx<<" sy " <<goal.sy<<" theta "<<goal.theta<<" kappa "<<goal.kappa);
curvature.success= FALSE;
}
else
{
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Converged in "<<iteration<<" iterations");
#ifdef LOG_OUTPUT
// Set time horizon
double horizon = curvature.s/v_0;
// Run motion model and log data for plotting
veh_next = motionModel(veh, goal, curvature, 0.1, horizon, 1);
fmm_sx<<"0.0 n";
fmm_sy<<"0.0 n";
#endif
}
return curvature;
}
lattice_twist_convert订阅车辆状态和规划输出,并发布到twist_cmd命令:
// Publish the following topics:
// Commands
ros::Publisher cmd_velocity_publisher = nh.advertise<geometry_msgs::TwistStamped>("twist_raw", 10);
// Subscribe to the following topics:
// Curvature parameters and state parameters
ros::Subscriber spline_parameters = nh.subscribe("spline", 1, splineCallback);
ros::Subscriber state_parameters = nh.subscribe("state", 1, stateCallback);
lattice_velocity_set可根据不同的路段和情况设置不同的车辆速度。
path_select用来实现换道:
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include "autoware_msgs/Lane.h"
#include <iostream>
static ros::Publisher _pub;
void callback(const autoware_msgs::Lane &msg)
{
_pub.publish(msg);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "path_select");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::Subscriber twist_sub = nh.subscribe("temporal_waypoints", 1, callback);
_pub = nh.advertise<autoware_msgs::Lane>("final_waypoints", 1000,true);
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
😆3. 应用示例

以上。
1. OpenPlanner介绍
OpenPlanner是Autoware种使用的一种运动规划算法,通过对全局路径采样后生成一系列的候选路径,结合矢量地图、传感器结构化数据以及碰撞、交通规则等约束和优化目标,选择出最优的运动轨迹。
OpenPlanner通用性强,只需相应的调整参数即可与任何的移动机器人/自动驾驶车辆车辆配合使用。
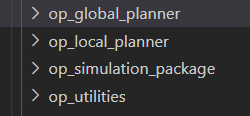
op有全局规划、局部规划以及仿真和工具模块。
2. 相关代码
op_global_planner全局规划也用到了DP动态规划算法,生成全局路径如下:
bool GlobalPlanner::GenerateGlobalPlan(PlannerHNS::WayPoint& startPoint, PlannerHNS::WayPoint& goalPoint, std::vector<std::vector<PlannerHNS::WayPoint> >& generatedTotalPaths)
{
std::vector<int> predefinedLanesIds;
double ret = 0;
ret = m_PlannerH.PlanUsingDP(startPoint, goalPoint, MAX_GLOBAL_PLAN_DISTANCE, m_params.bEnableLaneChange, predefinedLanesIds, m_Map, generatedTotalPaths);
if(ret == 0)
{
std::cout << "Can't Generate Global Path for Start (" << startPoint.pos.ToString()
<< ") and Goal (" << goalPoint.pos.ToString() << ")" << std::endl;
return false;
}
if(generatedTotalPaths.size() > 0 && generatedTotalPaths.at(0).size()>0)
{
if(m_params.bEnableSmoothing)
{
for(unsigned int i=0; i < generatedTotalPaths.size(); i++)
{
PlannerHNS::PlanningHelpers::FixPathDensity(generatedTotalPaths.at(i), m_params.pathDensity);
PlannerHNS::PlanningHelpers::SmoothPath(generatedTotalPaths.at(i), 0.49, 0.35 , 0.01);
}
}
for(unsigned int i=0; i < generatedTotalPaths.size(); i++)
{
PlannerHNS::PlanningHelpers::CalcAngleAndCost(generatedTotalPaths.at(i));
if(m_GlobalPathID > 10000)
m_GlobalPathID = 1;
for(unsigned int j=0; j < generatedTotalPaths.at(i).size(); j++)
generatedTotalPaths.at(i).at(j).gid = m_GlobalPathID;
m_GlobalPathID++;
std::cout << "New DP Path -> " << generatedTotalPaths.at(i).size() << std::endl;
}
return true;
}
else
{
std::cout << "Can't Generate Global Path for Start (" << startPoint.pos.ToString() << ") and Goal (" << goalPoint.pos.ToString() << ")" << std::endl;
}
return false;
}
op_local_planner局部规划包含op_trajectory_generator轨迹生成、op_trajectory_evaluator轨迹评价、op_behavior_selector行为选择和op_motion_predictor运动预测。
op_simulation_package是关于op的仿真包。
op_utilities是关于op相关工具,如op_pose2tf位姿坐标转换、op_data_logger数据记录和op_bag_player包播放工具。
以上。